In[1]:=
In[2]:=
Prepared by L. Kocbach
based on work of
James M. Feagin, Ladislav Kocbach, Richard Liska and Alonso Nunez
(1994-95)
Package for Clebsch Gordans
6-j package
Evaluation of Matrix elements between hydrogenic orbitals
Examples :Helium and helium like ions
Matrix Element of Particle-Electron Interaction
as function of Particle distance
Functions Defined
Clebsch[ {A , a }, {B , b }, {C , c } ] Clebsch-Gordan Coefficients
Threej[ {A ,a },{B ,b },{C ,c } ] Three-J Coefficients
Sixj[{A ,B , C },{a ,b ,c }] Six-J Coefficients
Redmat[A ,K ,B ] Reduced M.E. of 3 Spherical Harmonics
RadHyd[n , l , r , Z ] Radial Functions of Hydrogen-like ion with Z
MatEl[ Z , n1 , l1 , n2 , l2 , LL , rr ]
Matrix Element (Radial part) of a particle - electron interaction
DoubMatEl[Z ,n1 ,l1 ,n2 ,l2 ,n3 ,l3 ,n4 ,l4 ,L ] Redu
Matrix Element (Radial part) of electron - electron repulsion
Corremat[Z ,na ,la ,nb ,lb ,nc ,lc ,nd ,ld ,L ] Redu
Matrix Element (Total) of a electron - electron repulsion
Example 1
Helium and helium like ions, using variational method
Ekin[zvar ,n ]:=1/2 zvar^2/n^2 ; Epot[Zatom,zvar,n ]:=-zvar Zatom/n^2
Etot[Zatom ,zvar ,n ] -> 2 Ekin[zvar ,n ] + 2 Epot[Zatom,zvar ,n ] +
Corremat[zvar, n, 0, n, 0,n, 0,n, 0,0]
Solve[D[Etot[Znuc,z,1],z] == 0, z] Finds the effective Z by variational method
Example 2:
Matrix Element of Projectile-electron Interaction
as function of Particle-Nucleus distance
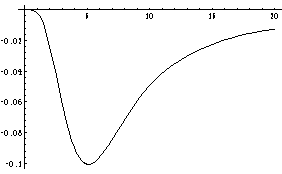
fff=MatEl[2,3,2,3,1,1,x];
Plot[fff,{x,0,20}] *)
In[3]:=
(* This is a Package of Clebsch Gordans : Origin James M. Feagin *)
(**** Uses Racah s formula to compute Clebsch-Gordan coefficient
and its related 3j symbol. Definitions of CG coefficient and
3j symbol are as in
BRINK & SATCHLER, “Angular Momentum,” 2nd ed., p.34, eq. 2.34,
and App. I, p.136.
****)
(**** Entered 1/26/91 constraints:
C < Abs[A-B] || C > A+B.
Abs[a] > A || Abs[b] > B || Abs[c] > C.
****)
BeginPackage["Quantum`Clebsch`"]
Clebsch::usage =
"Clebsch[{A,a},{B,b},{C,c}] gives the Clebsch-Gordan coefficient
for the addition of angular momenta C = A + B using Racah’s formula
(see Brink&Satchler, “Angular Momentum,” 2nd ed.(Oxford), p.34)."
Threej::usage =
"Threej[{A,a},{B,b},{C,c}] gives the 3-j symbol for
combining angular momenta, which is proportional to the CG coefficient."
Begin["`private`"]
(* see Brink&Satchler, p.140 *)
Clebsch[{A_,a_},{A_,b_},{0,0}] := (-1)^(A-a)/Sqrt[2A+1] /; b == -a
Clebsch[{A_,a_},{B_,b_},{0,0}] := 0
f1[C_,A_,B_,a_,b_] :=
Sum[ (-1)^k (k! (A+B-C-k)! (A-a-k)! (B+b-k)! (C-B+a+k)!
(C-A-b+k)!)^-1,
{ k, Max[0,B-C-a,A-C+b], Min[A+B-C,A-a,B+b] } ]
(* These Max and Min prevent the arguments of
Factorial (!) from becoming negative when the sum over k is
performed. *)
f2[C_,A_,B_] := (-C+A+B)! (C-A+B)! (C+A-B)! /(1+C+A+B)!
f3[C_,A_,B_,c_,a_,b_] := (1+2C) (C-c)! (C+c)! (A-a)! (A+a)! (B-b)! (B+b)!
(* see Brink&Satchler, p.34, eq. 2.34 *)
Clebsch[ {A_, a_}, {B_, b_}, {C_, c_} ] :=
If[ c!=a+b || C < Abs[A-B] || C > A+B ||
Abs[a] > A || Abs[b] > B || Abs[c] > C, 0 ,
Block[ {}, f1[C,A,B,a,b] Sqrt[ f2[C,A,B]
f3[C,A,B,c,a,b] ]
]
]
(* see Brink&Satchler, App. I, p.136 *)
Threej[ {A_,a_},{B_,b_},{C_,c_} ] :=
(-1)^(B-A+c)/Sqrt[2C+1] Clebsch[{A,a},{B,b},{C,-c}]
End[ ]
EndPackage[]
In[4]:=
(*This is a modification of the matrix elements evaluation to include Z- dependence :
Origin L. Kocbach and R. Liska; Modified by Alonso Nunez *)
Rad[n_ , l_ , r_ , Z_ ]:=
LaguerreL[n-l -1 , 2 l+1,2 Z r/n] Exp[- Z r/ n] ( Z r )^l
RadHyd[n_ , l_ , r_ , Z_ ] :=
Rad[n , l , r , Z ] / Sqrt[Norm2 [ n , l , Z ] ]
MatEl[ Z_, n1_ , l1_ , n2_ , l2_ , LL_ , rr_ ] :=
Block[
{ fun1, fun2, v, res1, res2, int1, int2 , res},
fun1=(RadHyd[n1,l1, v , Z]/. E->enat);
fun2=(RadHyd[n2,l2, v, Z ]/. E->enat);
res2=Integrate[Expand[v^2 fun1 fun2 / v^(LL+1)],v];
res1=Integrate[Expand[v^2 v^LL fun1 fun2],v];
int1=( res1/. v->rr) ;
int1= int1 - ( res1/.v->0);
int2= - res2/. v->rr ;
res = ( ( int1/rr^(LL+1) + rr^(LL) int2 )/. Log[enat]->1);
res/. enat->E
]
Norm2[n1_ , l1_ , Z_ ] :=
Block[
{ fun, v, res, int },
fun=(Rad[n1,l1, v, Z]/. E->enat);
res=Integrate[Expand[v^2 fun fun],v];
int = - res/. v->0 ;
res = int /. Log[enat]->1 ;
res/. enat->E ]
In[5]:=
DoubMatEl[Z_,n1_,l1_,n2_,l2_,n3_,l3_,n4_,l4_,L_] :=
Block[
{fun1,fun2, v, res, int },
fun1=(RadHyd[n1,l1, v ,Z]/. E->enat);
fun2=(RadHyd[n4,l4, v ,Z]/. E->enat);
fun3=(MatEl[Z,n2,l2,n3,l3,L,v]/. E->enat);
res=Integrate[Simplify[Expand[v^2 fun1 fun2 fun3 ]],v];
int = - res/. v->0 ;
res = int /. Log[enat]->1 ;
res/. enat->E
]
In[6]:=
(* Example *) DoubMatEl[1,1,0,1,0,1,0,2,0,0]
Out[6]=
25/2 2 ----- 64827
In[7]:=
DoubMatEl[1,2,0,1,0,4,0,3,0,0]//N
Out[7]=
0.00130335
In[8]:=
(*
First version of 6-j package :Using Cowan, page 147
Origin: Alonso Nunez
(* Special value for one J zero *)
Clebshing1[C_,A_,B_,a_,b_,0] := (-1)^(A+B+C)/Sqrt[(2A+1)(2B+1)]
In[9]:=
(* Used in general expression *)
ClebDelta2[C_,A_,B_] := (-C+A+B)! (C-A+B)! (C+A-B)! /(1+C+A+B)!
(* Used in general expression, Big Sum *)
ClebSum3[C_,A_,B_,c_,a_,b_] :=
Sum[ (-1)^k (k+1)! ((A+B+a+b-k)! (B+C+b+c-k)! (C+A+c+a-k)!
(k-A-B-C)! (k-A-b-c)! (k-a-B-c)! (k-a-b-C)!)^-1,
{ k, Max[0,A+B+C,A+b+c,a+B+c,a+b+C],
Min[A+B+b+a,A+B+b+c,C+A+c+a] } ]
In[10]:=
Sixj[{A_,B_, C_},{a_,b_,c_}] :=
If[ C < Abs[A-B] || C > A+B , 0 (* if not satisfied *),
Block[ (* if satisfied *)
{},
If [ c==0, Clebshing1[C,A,B,a,b,0] ,
Sqrt[ ClebDelta2[C,A,B]ClebDelta2[c,b,A]
ClebDelta2[c,a,B] ClebDelta2[C,a,b]]
ClebSum3[C,A,B,c,a,b] ]
] (* end block *)
] (* end if *)
In[11]:=
Redmat[A_,K_,B_] :=
(-1)^A Sqrt[(2A+1)(2B+1)] Threej[{A,0},{K,0},{B,0}]
Smrk[la_,lb_,lc_,ld_,L_,K_] :=
(-1)^(lc+lb+L) Sixj[{la,lb,L},{ld,lc,K}] Redmat[la,K,lc] Redmat[lb,K,ld]
Corremat[Z_,na_,la_,nb_,lb_,nc_,lc_,nd_,ld_,L_] :=
Sum[ Smrk[la,lb,lc,ld,L,K]
DoubMatEl[Z,na,la,nb,lb,nc,lc,nd,ld,K]
,{K, Max[0,Abs[la-lc],Abs[lb-ld]],
Min[la+lc,lb+ld] } ]
In[12]:=
(* Example *)
Corremat[1,3,2,3,2,4,0,4,0,0]/Corremat[64,3,2,3,2,4,0,4,0,0]
Out[12]=
1 -- 64
In[13]:=
(* z n1 l1 n2 l2 n3 l3 n4 l4 L *) (* Output Form *)
In[14]:=
Corremat[ 2, 1,0, 1,0, 1,0, 1,0, 0]
Out[14]=
5 - 4
In[15]:=
Corremat[ 2, 2,0, 1,0, 2,0, 1,0, 0]
Out[15]=
32 --- 729
In[16]:=
(* Example:
Helium and helium like ions, using variational method *)
Ekin[zvar_ ,n_ ] := 1/2 zvar^2/n^2
Epot[Zatom_,zvar_ ,n_ ]:= - zvar Zatom/n^2
Etot[Zatom_,zvar_ ,n_ ]:=
2 Ekin[zvar ,n ] + 2 Epot[Zatom,zvar ,n ] +
Corremat[zvar, n, 0, n, 0,n, 0,n, 0,0]
In[17]:=
Etot[2,2,1]
Out[17]=
11
-(--)
4
In[18]:=
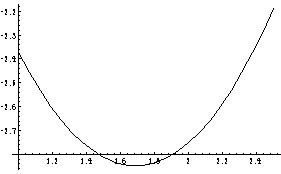
TRIAL=Etot[2,z,1]
Out[18]=
-27 z 2
----- + z
8
In[19]:=
Plot[TRIAL, {z, 1, 2.5}]

In[20]:=
D[Etot[2,z,1],z]
Out[20]=
27
-(--) + 2 z
8
In[21]:=
Solve[D[Etot[6,z,1],z] == 0, z]
%//N
Out[21]=
91
{{z -> --}}
16
Out[22]=
{{z -> 5.6875}}
In[23]:=
Zat=1; {Zat, Solve[D[Etot[Zat,z,1],z] == 0, z]//N }
Zat=2; {Zat, Solve[D[Etot[Zat,z,1],z] == 0, z]//N }
Zat=3; {Zat, Solve[D[Etot[Zat,z,1],z] == 0, z]//N }
Zat=4; {Zat, Solve[D[Etot[Zat,z,1],z] == 0, z]//N }
Zat=6; {Zat, Solve[D[Etot[Zat,z,1],z] == 0, z]//N }
Out[23]=
{1, {{z -> 0.6875}}}
Out[24]=
{2, {{z -> 1.6875}}}
Out[25]=
{4, {{z -> 3.6875}}}
Out[26]=
{6, {{z -> 5.6875}}}
In[27]:=
Solve[D[Etot[anyZ,z,1],z] == 0, z]
Out[27]=
-(5 - 16 anyZ)
{{z -> --------------}}
16
In[28]:=
First[Normal[Solve[D[Etot[anyZ,z,1],z] == 0, z] ]]
Out[28]=
-(5 - 16 anyZ)
{z -> --------------}
16
In[29]:=
(* Example 2:
Matrix Element of Interaction as function of
Internuclear distance *)
In[30]:=
fff=MatEl[2,3,2,3,1,1,x];
Plot[fff,{x,0,20}]