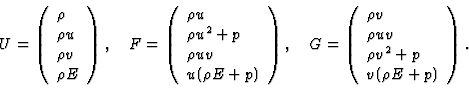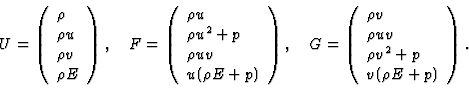Next: Riemann problems
Up: Composite Schemes for Conservation
Previous: Composite Schemes for Conservation
Gas dynamic tests
The Euler equations for an ideal gas in 2D are
Ut + F(U)x + G(U)y = 0,
where
Here 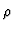 is the density, u the velocity in the x-direction,
v the velocity in the y direction,
E=e+1/2 (u2+v2) is the
total energy, e is the internal energy density, and
is the density, u the velocity in the x-direction,
v the velocity in the y direction,
E=e+1/2 (u2+v2) is the
total energy, e is the internal energy density, and
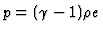 is the pressure.
is the pressure.
Richard Liska